Sec. 1.6 – Adding and Subtracting in Bases
Chapter 1, Section 6
Math Topics – Adding and Subtracting in Bases
Elementary Education – Understanding Adding and Subtracting in Base Ten Through Adding and Subtracting in Other Bases
In this section, we are going to dive deep into adding and subtracting in different bases. Why? Because that will help everyone understand adding in base ten more deeply, which will help guide how you teach your future students. It’s not just about “carry the 1”! It’s about math making sense — for everyone!
Adding in Base 5
In the previous homework, we issued a counting challenge! If you are counting in base 5, what’s the next number after 1245?
This is that same as asking for the answer to
1245
+ 15
Think about the Bizz buzz counting game!

Example 1 Count one more than 1245 using the Bizz Buzz game.
The number 1245 means we have counted one buzz, 2 bizzes, and then counted to 4 after that:
| Buzz | Bizz | Ones |
| 1 | 2 | 4 |
To count one higher, the next person might want to say 5, but in Buzz Buzz, we can’t say 5, so instead they must say “bizz.” Now we have counted to 3 bizzes.
| Buzz | Bizz | Ones |
| 1 | 3 | 0 |
Example 2 Add 1245 + 1 using base 5 blocks and trading.

In base 5, when you get 5 units, you can trade them for 1 rod.
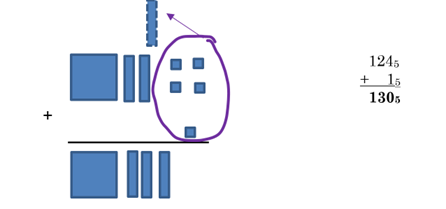
We can also show this as “carrying the 1”:
1
1245
+ 15
1305
This is the same answer as one buzz, 3 bizzes, and no ones.
The general principle, when adding in base 5, is to gather five of one kind of block to trade for one of the next higher block.
Example 3 Add 1415 + 1325 using base 5 blocks and trading.
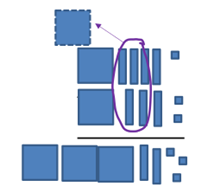
First we add the ones: 1 + 2 is 3, with no trading needed. Then we add 4 rods + 3 rods. We trade 5 of the rods for 1 flat, and we have two left over. Finally, we add the flats 1+1+1 = 3 flats. This is the base 5 number 3235.
We can also show the trading as “carrying the 1”:
1
1415
+ 1325
3235
Adding in Bases
What about if we are in a base other than 5?
Adding in other bases is similar to base 5, except that we use our base as our trading amount. For example, in base 7 we would trade 7 of an object for one of the next object higher: 7 units for a rod, 7 rods for a flat, and so forth. In base 8, we trade 8 for 1, and in base 3, we trade 3 for one. In base 12, we would have to have 12 of an object in order to trade for one of the next higher place value.
In each base, when we get up to the base value, we trade for one of the next higher place value.
Example 4 Try adding each of the following.
You can draw the blocks, or add without them – it’s your choice. It is okay to keep using the blocks for as long as you need, even the whole semester! It is not a bad thing to need a physical representation. (I don’t think counting on your fingers is bad, either!)
| Base 7 | Base 8 | Base 3 | Base 12 | |||
| 1647 + 1517 |
2678 + 4648 |
1113 + 2023 |
56712 + 7312 |
Here is the first problem, written in base 7 blocks, with the grid on each block shown, so you can see the size:
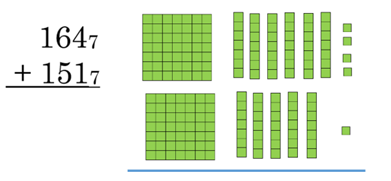
To add, first gather together all the units. Do you have enough units, that when you put them together, you would have 1 whole rod? What about the rods, do you have enough rods, that if you put them together, you would have a flat? Find the answer using the blocks, then look below for the result. Try the other base problems in a similar way.
Try each one before looking below for the answer.
Tip for the base 12 problem — do not trade unless you have 12 or more!
| Base 7 | Base 8 | Base 3 | Base 12 | |||
| 1 1647 + 1517 3457 |
1 1 2678 + 4648 7538 |
1 1 1113 + 2023 10203 |
1 56712 + 7312 61T12 |
Blocks for the first problem, in base 7, are shown below.
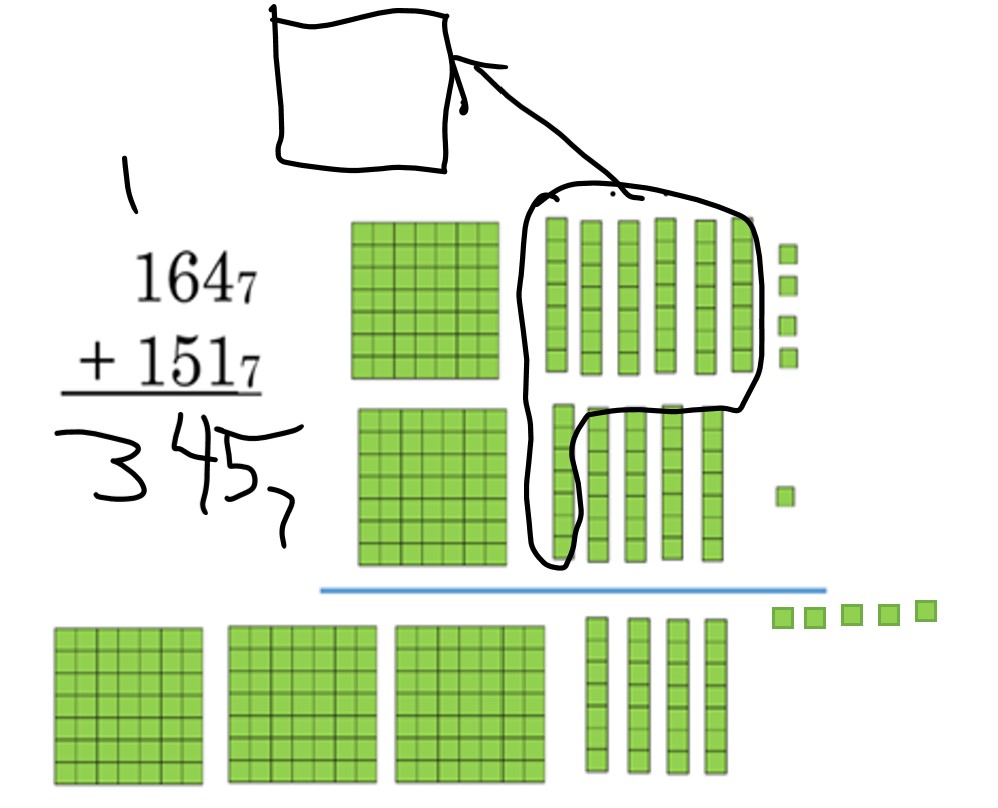
Notice that for the base 12 problem, 7 + 3 = 10, which is not enough to trade. Write T (or any other letter for 10) in that column. Remember that you cannot write 611012 instead of 61T12 because 611012 looks like 0 in the ones place instead of ten in the ones place.
Subtracting in Bases
Subtracting in base 5 works very similarly to adding in base 5, but now we trade in the other direction: we trade one for five of the next smaller sized block.
Example 5 Subtract 1205 – 1 using base 5 blocks and trading.
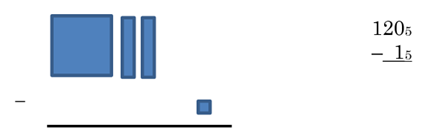
We can’t take away one unit as this is, so we trade 1 rod for 5 units.
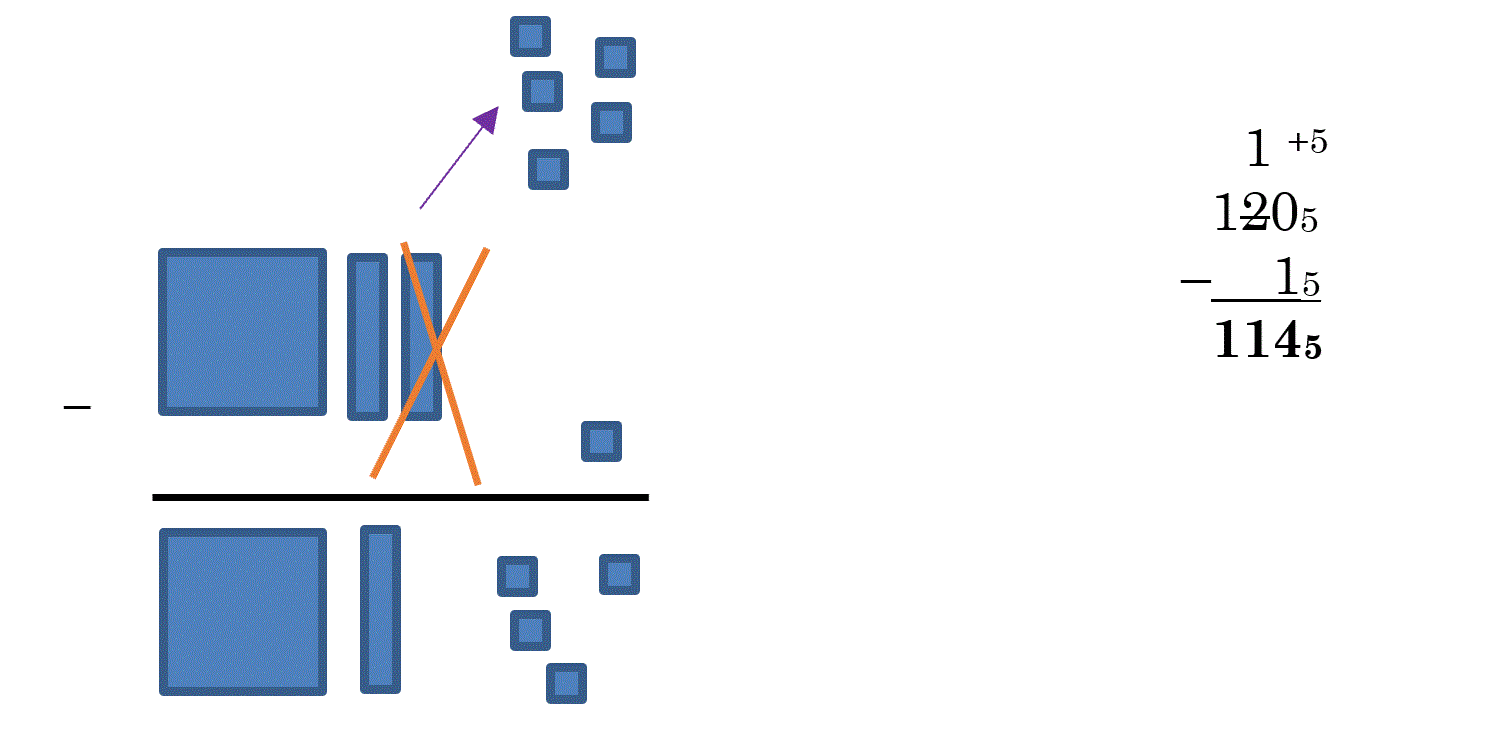
The 5 new units can now allow us to subtract 1 unit to get 4 units. We end up with 1 flat, one rod (since we traded a rod) and 4 units. The “short” version of this is to take 1205, cross out the 2 and make it a 1, then add 5 ones to the zero.
| 1 – 15 1145 |
Take a moment to appreciate how confusing it would have been if we had introduced base 5 subtraction to you that way! Yes, it’s great if you can get to be able to do that, but it’s also not necessary. What’s necessary is understanding what you are doing!
Example 6 Try subtracting each of the following.
You can draw the blocks, or subtract without them. In each problem, if we do not have enough up top to subtract from, we trade one for the base value in the next lower place value. In other words, in base 7, we trade 1 for 7, in base 8, we trade 1 for 8, etc.
| Base 7 | Base 8 | Base 3 | ||
| 2347 – 1517 |
56312 – 2712 |
4128 – 2678 |
Here is the first problem, written in base 7 blocks, with the grid on each block shown, so you can see the size:
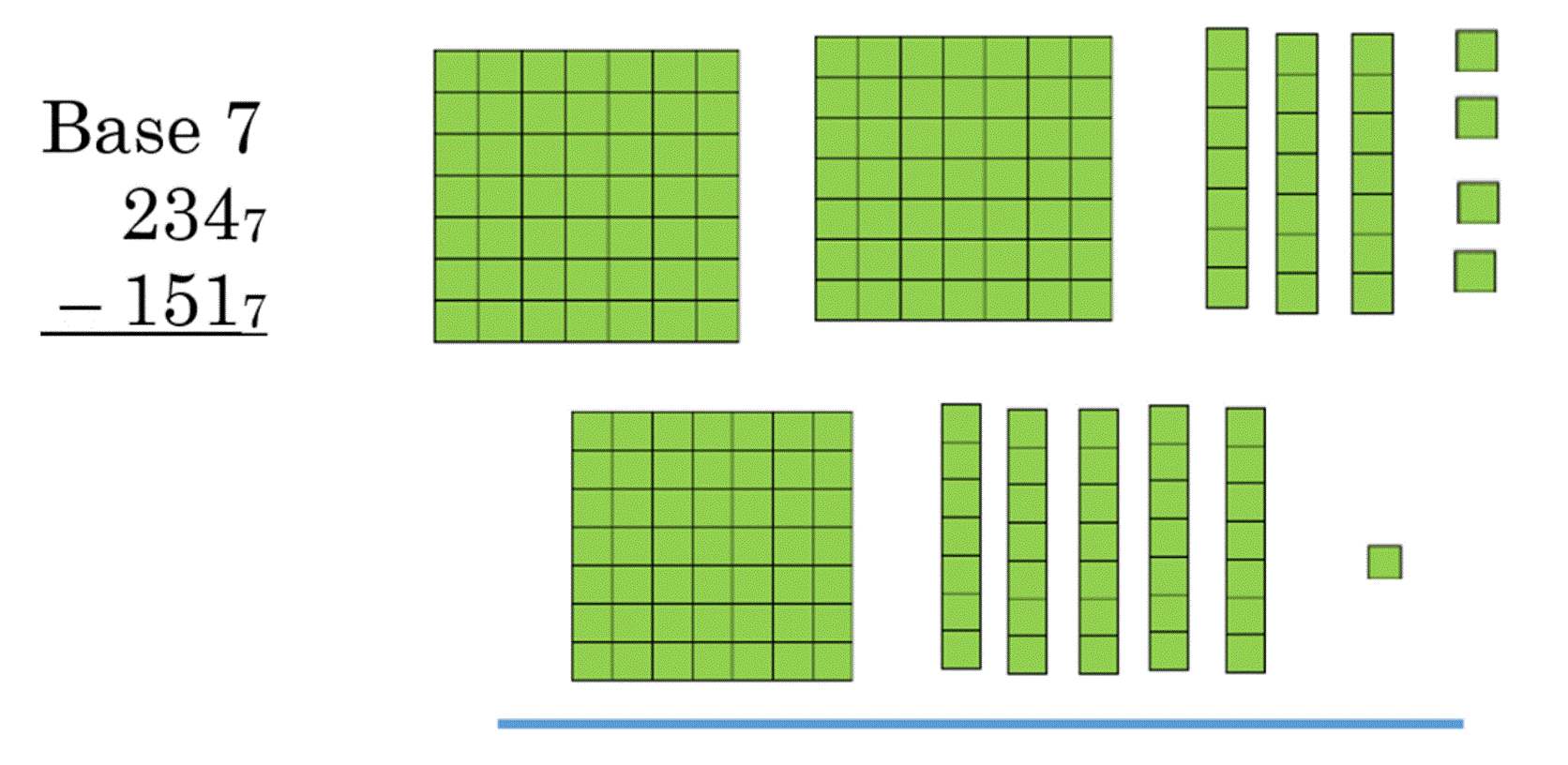
To subtract, ask yourself if you have enough up top to take the bottom blocks away. If not, break apart one of the bocks of the next size up. Remember that it is okay to draw blocks for each problem, if that is what you need to do to understand it.
Look below for the answers.
| Base 7 | Base 12 | Base 8 | ||
| 1 +7 2347 – 1517 537 |
5 +12 56312 – 2712 53812 |
3 +87 +8 4128 – 2678 1238 |
It may be difficult to understand each step shown up, just as when we tell children to “borrow from the 2” in base ten subtraction, so let’s look at the first one of these with the blocks for that base.
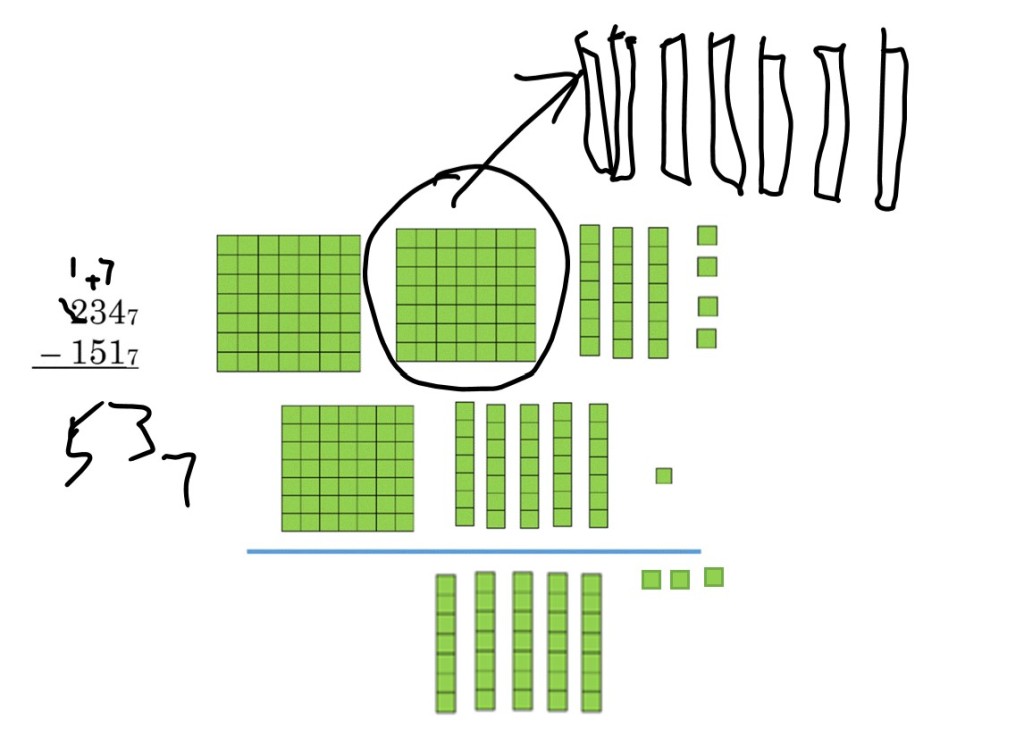
In this base 7 example, we started with 4 units minus one unit, to get three units. In the next place value, we didn’t have enough rods up top to be able to subtract 5 rods, so we broke apart on of the flats into 7 rods, and added those to the three we already had. Then we could subtract 10 rods – 5 rods = 5 rods.
Adding and Subtracting in binary

In binary (base 2), you can only have a 1 or a 0 for a result.
Example 7 Add 12 + 12 in base 2
When you add 1 + 1 you get 2, which you trade for one in the next column, with 0 left:
12
+ 12
102
You could also convert to see why this works: in base 10, 1 + 1 = 2, which converts to 102.
| 22 = 4 | 21 = 2 | 20 = 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Example 8 Subtract 102 – 12 in base 2
+2
102
– 12
12
Here, we have to “borrow” from the 1 in order to subtract. We trade the 1 for 2 in the smaller place value.