Chapter 4: Understanding International Classification of Diseases Taxonomy
Learning Objectives:
- Define ICD-10 and explain its purpose in the healthcare industry.
- Describe the structure of ICD-10, including chapters, categories, and codes.
- Explain the use of clinical modifications in ICD-10, such as ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS.
- Understand the apply the principles of hierarchy, specificity, external causes, and laterality in ICD-10 coding.
- Identify the benefits and limitations of ICD-10, such as improved accuracy of diagnoses and increased complexity of coding.
- Differentiate between ICD-10 and its predecessor, ICD-9, including the differences in structure, coding conventions, and clinical modifications.
- Identify the relevant codes for common medical conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, and asthma.
- Examine the impact of ICD-10 on healthcare, including the effects on coding accuracy, reimbursement, and healthcare data analysis.
In understanding the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), it is essential to grasp its structured taxonomy. The ICD-10 is organized hierarchically, starting with 22 broad chapters that categorize diseases and health-related conditions. Each chapter is further subdivided into blocks of three-character categories which denote specific disease groups or conditions. These categories are then broken down into four-character subcategories, providing further granularity. The most detailed level of classification is represented by the full code, which includes up to seven characters and specifies a particular disease entity or condition with precise detail. This systematic classification system forms the backbone of medical coding and billing worldwide, facilitating accurate documentation of diseases, injuries, and other health conditions. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in healthcare policy formulation and epidemiological research, providing standardized data that are crucial for understanding health trends, allocating resources, and developing effective public health strategies. By comprehending the structure and utility of the ICD-10 taxonomy, one gains a foundational understanding of its broad applications across the healthcare landscape.
Use of ICD-10 in Healthcare Settings Worldwide
The ICD-10 coding system serves as the universal diagnostic language across healthcare settings worldwide, essential for accurately classifying and coding diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures conducted in hospitals and various healthcare facilities. Maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO), this comprehensive system is adopted by countries globally for its role in epidemiological research, reimbursement processes, and statistical analysis. Healthcare providers rely on ICD-10 codes to document patient encounters systematically, ensuring clear communication across medical teams and facilitating accurate billing and reimbursement. Researchers utilize ICD-10 data to study disease patterns and trends, while policymakers use it to inform healthcare policies and resource allocation. As a result, ICD-10 codes are integral to the operations of healthcare providers, payers, researchers, and global public health officials, highlighting the foundation of modern healthcare management and analysis.
Benefits of Using the ICD-10 Coding System in the Healthcare System
The adoption of the ICD-10 coding system in the healthcare industry brings numerous benefits that enhance patient care and resource management. By providing a standardized and systematic framework for recording and reporting medical diagnoses and procedures, ICD-10 enables healthcare providers to communicate effectively and precisely across disciplines and settings. This consistency not only reduces errors in documentation but also supports efficient data analysis on health trends and outcomes, aiding in the development of targeted interventions and treatment protocols. Healthcare organizations benefit from ICD-10 by accurately tracking the resources utilized in patient care, which is crucial for budgeting, resource allocation, and reimbursement purposes. Ultimately, the implementation of ICD-10 promotes streamlined operations within healthcare systems, improves the quality of care delivered to patients, and supports informed decision-making at both clinical and administrative levels.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think standardized coding systems like ICD-10 help healthcare providers communicate more effectively and accurately about patient diagnoses and procedures?
- Why is it important for healthcare organizations to track resources using systems like ICD-10? How might this information impact budgeting and decision-making within a healthcare facility?
Role of ICD-10 Codes in Medical Billing and Insurance Claims
ICD-10 codes play a pivotal role in the medical billing and insurance claims process by accurately documenting and categorizing diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures performed during patient care. These standardized codes ensure that healthcare providers can submit claims to insurance companies with precise information regarding the services rendered. By linking specific ICD-10 codes to each medical service or procedure, providers facilitate accurate reimbursement from insurance providers, reducing billing errors and disputes. This systematic approach not only ensures healthcare facilities receive fair compensation for their services but also helps insurance companies assess the appropriateness of treatments and procedures. Ultimately, the use of ICD-10 in medical billing and insurance claims contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare operations, supporting improved patient care and financial management across the industry.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think using standardized codes like ICD-10 helps healthcare providers and insurance companies communicate effectively about medical services and reimbursement?
- Why is it important for healthcare facilities to accurately document diagnoses and procedures using ICD-10 codes in the billing process? How might this impact patient care and financial stability for healthcare organizations?
Understanding the Structure of ICD-10
The structure of ICD-10, overseen by the World Health Organization (WHO), is organized into 22 chapters that categorize a wide array of diseases and health conditions. Each chapter is dedicated to specific organ systems or groups of related conditions, such as infectious and parasitic diseases, neoplasms, diseases of the circulatory and respiratory systems, mental and behavioral disorders, and injury and poisoning. Numbered sequentially from I to XXII, these chapters provide a systematic framework for classifying medical diagnoses and procedures globally. Understanding these chapters is crucial for healthcare professionals as it ensures accurate coding and documentation of patient conditions, facilitating effective communication among medical teams, and supporting various healthcare management and research activities worldwide.
Table 1: Chapters of ICD-10
|
Chapter Number |
Chapter Title |
|
I |
Certain infectious and parasitic diseases |
|
II |
Neoplasms |
|
III |
Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism |
|
IV |
Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases |
|
V |
Mental and behavioral disorders |
|
VI |
Diseases of the nervous system |
|
VII |
Diseases of the eye and adnexa |
|
VIII |
Diseases of the ear and mastoid process |
|
IX |
Diseases of the circulatory system |
|
X |
Diseases of the respiratory system |
|
XI |
Diseases of the digestive system |
|
XII |
Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue |
|
XIII |
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue |
|
XIV |
Diseases of the genitourinary system |
|
XV |
Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium |
|
XVI |
Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period |
|
XVII |
Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities |
|
XVIII |
Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified |
|
XIX |
Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes |
|
XX |
External causes of morbidity and mortality |
|
XXI |
Factors influencing health status and contact with health services |
|
XXII |
Codes for special purposes |
These chapters provide a structured classification system for diseases and conditions, aiding in medical coding, epidemiological research, and healthcare management worldwide.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think organizing diseases into chapters like infectious diseases and mental disorders helps healthcare providers treat patients more effectively?
- Why do you think it’s important for medical coding systems like ICD-10 to have specific chapters for conditions such as injuries and congenital disorders? How might this organization benefit healthcare providers and researchers?
Categories and Codes in ICD-10
In ICD-10, each chapter is subdivided into categories, which serve as specific groupings of diseases and conditions identified by a three-digit code. These categories represent clusters of related conditions within broader organ systems or disease groups, such as diseases of the urinary system or disorders of the nervous system. Within each category, there are codes—alphanumeric designations ranging from four to seven digits—that provide detailed specificity about particular diagnoses or procedures. The first three digits of the code indicate the category to which the condition belongs, while the additional digits offer further granularity. These codes play a crucial role in medical coding and billing processes, facilitating accurate documentation for healthcare reimbursement and supporting research and public health initiatives by tracking disease prevalence and treatment outcomes. Understanding and correctly applying these codes in ICD-10 is essential for ensuring standardized healthcare data collection and analysis across global healthcare systems.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think using categories and codes in ICD-10 helps healthcare providers and researchers organize information about diseases and conditions?
- Why is it important for healthcare professionals to understand both the categories and specific codes in ICD-10 when documenting patient diagnoses and procedures? How might this knowledge impact patient care and healthcare management?
Use of Clinical Modifications in ICD-10
Clinical Modifications (CM) of ICD-10 are specialized adaptations tailored to meet the specific requirements of healthcare settings, particularly in the United States. There are two main types: ICD-10-CM for diagnosis coding and ICD-10-PCS for procedure coding. ICD-10-CM expands upon the original ICD-10 classification by including additional codes that provide more detailed information about diagnoses. These codes can be up to seven characters long, with the first three characters indicating the category. Understanding ICD-10-CM is crucial for healthcare providers in the U.S. as it ensures accurate diagnosis coding for medical billing and reimbursement purposes.
On the other hand, ICD-10-PCS is designed specifically for coding medical procedures in hospital inpatient settings. Each of its seven characters signifies a different aspect of the procedure, offering precise details necessary for billing and administrative purposes. Unlike the broad applicability of the standard ICD-10 system worldwide, both ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS cater specifically to the intricacies of healthcare practice in the United States, supporting efficient healthcare management and accurate financial transactions within hospital and clinical environments. Understanding these clinical modifications is essential for healthcare professionals involved in coding, billing, and policy-making processes within the U.S. healthcare system.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think using clinical modifications like ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS helps hospitals and clinics in the United States manage medical coding and billing more effectively?
- Why is it important for healthcare providers in the U.S. to understand the differences between ICD-10 and its clinical modifications, ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS? How might this knowledge impact patient care and healthcare administration?
Hierarchy in ICD-10 Coding
In the context of ICD-10, hierarchy refers to the structured ranking of codes based on their level of specificity. This hierarchical arrangement ensures that each code represents a distinct and precise diagnosis or condition. Healthcare providers are encouraged to code to the highest level of specificity available within the ICD-10 system, as this practice enables accurate identification of the patient’s diagnosis. A higher level of specificity not only aids in determining appropriate treatment options but also supports effective healthcare management and decision-making. By adhering to the hierarchy of ICD-10 codes, healthcare professionals can enhance patient care by providing tailored treatments and interventions based on detailed and accurate diagnostic information.
Examples of the ICD-10 Hierarchy
|
Code Range |
Disease Category |
|
A00-B99 |
Certain infectious and parasitic diseases |
|
A00-A09 |
Intestinal infectious diseases |
|
A00 |
Cholera |
|
A01 |
Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers |
|
A02 |
Other salmonella infections |
|
A03 |
Shigellosis |
|
A04 |
Other bacterial intestinal infections |
|
A05 |
Other bacterial foodborne intoxications |
|
A06 |
Amoebiasis |
|
A07 |
Other protozoal intestinal diseases |
|
A08 |
Viral and other specified intestinal infections |
|
A09 |
Diarrhoea and gastro-enteritis of presumed infectious origin |
|
B00-B09 |
Viral infections characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions |
|
B00 |
Herpesviral [herpes simplex] infections |
|
B01 |
Varicella [chickenpox] |
|
B02 |
Zoster [herpes zoster] |
|
B03 |
Smallpox |
|
B04 |
Monkeypox |
|
B05 |
Measles |
|
B06 |
Rubella [German measles] |
|
B07 |
Viral warts |
|
B08 |
Other viral infections characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions, not elsewhere classified |
|
B09 |
Other viral infections |
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10).
Discussion Questions
- How do you think organizing infectious diseases into categories and codes in ICD-10 helps healthcare providers diagnose and treat patients more effectively?
- Why is it important for healthcare professionals to understand the hierarchy of ICD-10 codes when documenting infectious diseases like cholera or measles? How might this knowledge improve healthcare outcomes and public health responses?
Specificity in ICD-10 Coding
Specificity in ICD-10 refers to the degree of detail provided in diagnostic codes, crucial for accurately describing a patient’s condition. A more specific code offers comprehensive information about the diagnosis, enabling healthcare providers to understand the nuances of the patient’s illness and select appropriate treatment strategies. For instance, the code 110 indicates essential (primary) hypertension, while the code 110.0 specifies essential (primary) hypertension with renal involvement. This higher level of specificity not only aids in clinical decision-making but also supports efficient healthcare management and resource allocation. By documenting conditions with precise codes, healthcare professionals can enhance patient care by ensuring tailored interventions that address the specific aspects of each individual’s health needs.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think using specific codes in ICD-10, like those for hypertension with renal involvement versus general hypertension, helps doctors choose the best treatments for patients?
- Why is it important for healthcare providers to document diagnoses with detailed specificity in ICD-10? How might this level of detail impact patient care and overall healthcare quality?
External Causes in ICD-10 Coding
In ICD-10, external causes codes serve the purpose of identifying and documenting the specific causes of injuries or health conditions that are not inherently disease-related. These codes provide valuable information about the circumstances surrounding an injury or condition, offering insights into how and why it occurred. By including external causes in documentation, healthcare providers can accurately record details such as accidents, falls, assaults, or environmental exposures that contributed to a patient’s health issue. This comprehensive approach not only aids in understanding the root causes of injuries but also supports preventive measures and public health initiatives aimed at reducing the incidence of these events. Therefore, incorporating external causes codes in ICD-10 enhances the overall quality of healthcare by facilitating targeted interventions and promoting safety awareness in various settings.
Example of External Causes Code in ICD-10: V01.0 used to describe a pedestrian injured in a collision with a pedal cycle.
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10).
Discussion Questions
- How do you think using external causes codes in ICD-10 helps healthcare providers and researchers understand the circumstances of injuries or health conditions?
- Why is it important for healthcare professionals to accurately document external causes, like accidents or environmental exposures, in ICD-10? How might this information contribute to improving patient care and preventing future incidents?
Laterality in ICD-10 Coding
Laterality in ICD-10 refers to specifying which side of the body is affected by a particular condition or symptom. This aspect is particularly relevant for conditions that occur in paired body parts, such as ears, knees, or shoulders. Accurate documentation of laterality ensures precise diagnoses and enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans accordingly. For example, the code M25.552 indicates pain in the left hip, while M25.562 specifies pain in the right hip. Understanding laterality in ICD-10 coding is essential for healthcare professionals to effectively communicate patient conditions, ensuring appropriate care and management strategies. Properly coding for laterality also supports accurate billing and reimbursement processes, aiding in financial operations within healthcare facilities and contributing to comprehensive healthcare data analysis and research efforts.
Discussion Questions
- Why do you think it’s important for healthcare providers to specify laterality in conditions like hip pain or ear infections when using ICD-10 codes? How might this detail affect patient treatment and care?
- How can understanding laterality in ICD-10 coding help healthcare administrators and researchers track health trends more accurately? What are some potential benefits of having detailed information about which side of the body is affected by a condition?
Benefits and Limitations of ICD-10
ICD-10, as a globally adopted classification system for healthcare data reporting, offers significant benefits and some limitations. One of its primary advantages is the enhancement of accuracy, consistency, and comparability in healthcare data. This standardized approach enables healthcare professionals to document diagnoses and procedures uniformly, facilitating better communication among providers and supporting comprehensive health analyses at local, national, and global levels. Policymakers can utilize ICD-10 data to identify health trends, allocate resources effectively, and develop evidence-based policies aimed at improving public health outcomes and patient care.
However, ICD-10 also presents challenges. Its comprehensive structure and detailed coding requirements can be complex, requiring thorough training and expertise from healthcare coders and providers. The potential for coding errors remains a concern, which could impact billing accuracy and data integrity. Moreover, the interpretation of clinical information and the assignment of codes may sometimes involve subjective judgment, leading to variability in coding practices across different healthcare settings. Despite these limitations, understanding both the benefits and challenges of ICD-10 is essential for healthcare professionals to maximize its utility in supporting high-quality patient care and advancing public health initiatives effectively.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think the adoption of ICD-10 helps healthcare providers and policymakers improve patient care and public health decisions? What are some specific examples?
- What challenges do healthcare professionals face when using ICD-10 for coding and reporting healthcare data? How might these challenges be addressed to enhance the effectiveness of the system?
Impact of ICD-10 on Healthcare
The adoption of ICD-10 has had a profound impact on healthcare across various domains. With its increased specificity and detailed coding structure compared to ICD-9, ICD-10 has significantly enhanced the accuracy and thoroughness of clinical documentation and medical billing processes. This improvement allows healthcare providers to capture more precise information about patient diagnoses and procedures, which in turn supports better treatment planning and patient outcomes. However, the transition to ICD-10 has not been without challenges. Healthcare organizations have faced hurdles such as the need for extensive staff training, adjustments to documentation practices, and potential disruptions in revenue cycles due to coding and billing complexities. Despite these challenges, the overall impact of ICD-10 has been beneficial, enabling healthcare providers and organizations to leverage more robust data for research, quality reporting, and healthcare policy development, ultimately aiming to improve overall healthcare delivery and patient care.
Discussion Questions
- How has the transition to ICD-10 impacted the way healthcare providers document and treat patient conditions compared to the previous ICD-9 system?
- How do you think the increased specificity and detail in ICD-10 coding have improved healthcare data accuracy and patient care outcomes?
Differences between ICD-10 and ICD-9
ICD-10 and ICD-9 represent distinct phases in the evolution of medical coding systems, each with its own structure, coding conventions, and clinical modifications. One of the primary differences lies in their coding formats: ICD-9 utilizes three to five-digit numeric codes, whereas ICD-10 employs a more detailed seven-digit alphanumeric coding system. This allows ICD-10 to provide greater specificity and granularity in describing medical diagnoses and procedures, thereby enhancing the accuracy and precision of healthcare data.
ICD-10 also introduces new coding conventions compared to ICD-9. While ICD-9 codes are only numeric, ICD-10 incorporates alphanumeric characters to offer more detailed information about the condition being coded. Moreover, ICD-10 includes combination codes that can capture multiple conditions and their related symptoms within a single code, streamlining documentation and improving the comprehensiveness of medical records. Additionally, ICD-10 codes may include additional details such as laterality (indicating which side of the body is affected), episode of care, and other clinical factors that were not captured in the older ICD-9 system.
ICD-10 further expands its utility with clinical modifications that were absent in ICD-9. Notably, ICD-10-CM (Clinical Modification) incorporates supplementary codes for diseases and conditions, reflecting advances in medical knowledge and technology. Meanwhile, ICD-10-PCS (Procedure Coding System) introduces more specific codes for medical procedures, facilitating precise tracking of healthcare utilization and outcomes. These enhancements enable healthcare providers and policymakers to gather more comprehensive data for research, quality improvement initiatives, and healthcare planning.
In summary, while both ICD-10 and ICD-9 serve the fundamental purpose of classifying medical conditions and procedures, the transition to ICD-10 signifies a significant leap forward in terms of coding specificity, clinical detail, and adaptability to evolving healthcare practices. While this transition has brought substantial benefits to healthcare delivery and data analysis, it has also posed challenges for healthcare organizations adapting to the new coding standards and requirements.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think the increased specificity of ICD-10 codes compared to ICD-9 helps healthcare providers in diagnosing and treating patients more accurately?
- Why is it important for healthcare organizations to adapt to the alphanumeric format of ICD-10 codes compared to the numeric format of ICD-9? How might this change impact medical billing and data accuracy?
- What are some potential benefits of ICD-10’s inclusion of laterality, episode of care, and other clinical factors that were not present in ICD-9? How might these enhancements improve healthcare decision-making and patient outcomes?
Generating ICD-10 Codes for Medical Conditions
Generating accurate ICD-10 codes for medical conditions like Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, and Asthma is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment planning in healthcare settings. For Diabetes Mellitus, determining the appropriate code involves specifying the type of diabetes (such as Type 1, Type 2, or other specified types), noting any complications associated with the condition, and identifying whether insulin is being used by the patient. For instance, codes like E10.9, E11.9, and E13.9 are used for Type 1, Type 2, and other specified Diabetes Mellitus without complications, respectively (Video 1).
“Video 1: ICD-10 Coding and Diabetes” by CMSHHSgov, The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is in the Public Domain, CC0
Similarly, coding for Hypertension requires detailed information about the type of hypertension (e.g., essential hypertension), any related complications (such as hypertensive heart disease or chronic kidney disease), and whether the condition is controlled or uncontrolled. Codes such as I10, I11.9, I12.9, and I13.10 are examples used to specify different aspects and complexities of hypertensive conditions, aiding in accurate diagnosis and management decisions.
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, also demands precise coding to reflect its type (e.g., mild intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, severe persistent), any associated complications, and the severity of the asthma attacks. Codes like J45.20, J45.21, J45.22, and J45.23 are utilized to capture the varying degrees of severity and management needs in asthma patients.
In summary, generating ICD-10 codes involves understanding the nuances of each medical condition, including type, complications, and severity, to ensure accurate documentation and proper treatment planning. Consulting ICD-10 guidelines and coding manuals is essential to navigate the vast array of codes available and to uphold coding accuracy in clinical practice.
Discussion Questions
- How might accurate ICD-10 coding for conditions like Diabetes Mellitus and Asthma help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to meet individual patient needs? What specific information would you need to determine the correct code for each condition?
- Why is it important for healthcare professionals to understand the differences between ICD-10 codes for conditions like Hypertension, which include details about complications and severity? How might these details impact patient care and management?
- What challenges might healthcare organizations face when transitioning from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding systems for documenting medical conditions? How can these challenges be addressed to ensure smooth implementation and accurate coding?
Impact of ICD-10 on Coding Accuracy, Reimbursement, and Healthcare Data Analysis
ICD-10 has significantly enhanced coding accuracy, reimbursement processes, and healthcare data analysis compared to its predecessor, ICD-9. The system’s more specific and detailed codes allow healthcare providers to accurately document diagnoses and procedures, leading to improved medical records that support better patient care and outcomes. Moreover, the increased specificity in ICD-10 coding has facilitated more precise billing and reimbursement practices. Although the transition to ICD-10 initially caused delays and disruptions in reimbursement as healthcare organizations adjusted to the new coding requirements, overall, it has contributed to greater reimbursement accuracy and reduced instances of fraud and abuse in healthcare billing practices.
ICD-10’s detailed and specific coding structure has also revolutionized healthcare data analysis. Researchers and policymakers now have access to richer data sets that enable them to identify healthcare trends more accurately and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. This capability is particularly evident in public health initiatives such as tracking the opioid epidemic, where ICD-10’s detailed coding allows for better monitoring and understanding of the impact of opioid-related conditions and treatments. As healthcare continues to evolve, the continued use and refinement of ICD-10 are expected to further enhance healthcare delivery and outcomes by leveraging comprehensive data analytics to inform targeted improvements in patient care and public health strategies.
Discussion Questions
- How do you think the increased specificity of ICD-10 codes compared to ICD-9 has improved coding accuracy in healthcare? What benefits does more accurate coding bring to patient care and reimbursement?
- Why is it important for healthcare researchers and policymakers to have access to detailed healthcare data analysis facilitated by ICD-10? How can this data help in addressing public health challenges and improving healthcare delivery?
Emergency Use ICD Codes: Tracking Diseases in Outbreaks
Emergency use ICD codes, exemplified by their application during the COVID-19 pandemic, serve as essential tools for swiftly categorizing and monitoring diseases during outbreaks. These codes enable healthcare providers and public health authorities to efficiently report and track the spread of diseases, thereby facilitating a coordinated response to mitigate their impact on public health and healthcare systems. Throughout the COVID-19 outbreak, emergency use ICD codes were swiftly developed by the WHO to standardize the reporting of cases across diverse healthcare settings globally. These codes encompassed categories for suspected, confirmed, and possible cases of COVID-19, alongside codes for associated complications and sequelae. By utilizing these codes, healthcare systems could effectively monitor disease transmission, assess case severity, and gauge the strain on healthcare resources. Overall, emergency use ICD codes have played a critical role in providing accurate data to inform public health strategies and research efforts aimed at combatting the COVID-19 pandemic.
Emergency Use ICD Codes for COVID-19 Disease Outbreak
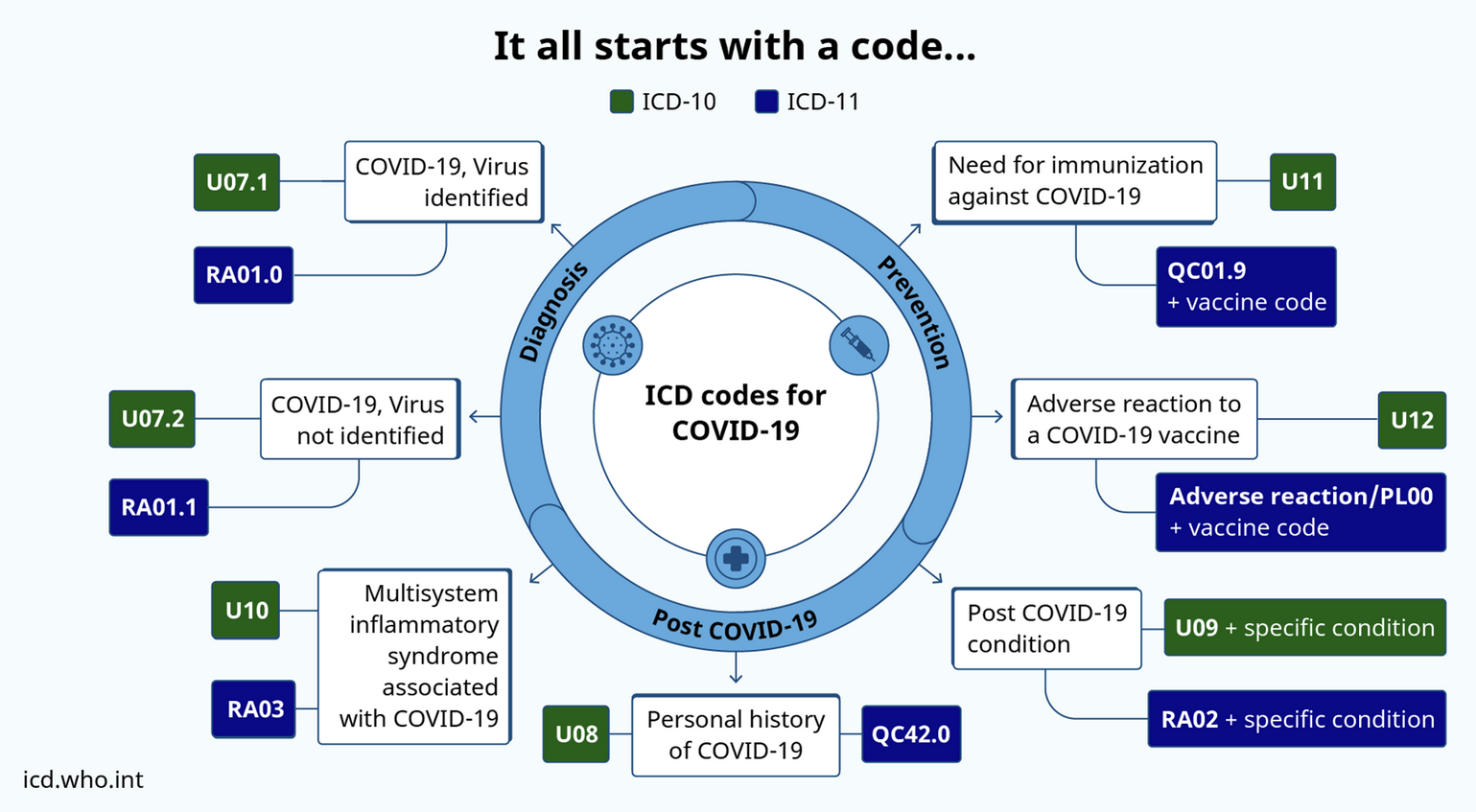
Source: WHO (2022). International Classification of Disease (ICD). Emergency Use ICD Codes for COVID-19 Disease Outbreak
Key Terms
ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision; a globally used system for classifying diseases and health-related conditions maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Hierarchical Structure: Organizational framework of ICD-10 starting with broad chapters, followed by categories, subcategories, and specific codes, ensuring systematic classification.
Chapters: 22 broad divisions in ICD-10 categorizing diseases and health conditions based on organ systems or related groups.
Categories: Three-character groups within each chapter representing specific disease groups or conditions.
Codes: Alphanumeric designations ranging from four to seven characters in ICD-10, providing detailed specificity about diagnoses or procedures.
Clinical Modifications: Adaptations of ICD-10 tailored for specific healthcare settings, such as ICD-10-CM (for diagnoses) and ICD-10-PCS (for procedures).
Hierarchy Principle: Coding guideline in ICD-10 encouraging the use of the most specific code available to accurately reflect diagnoses or procedures.
Specificity: Degree of detail provided in ICD-10 codes, crucial for precise documentation and treatment planning.
External Causes: ICD-10 codes identifying factors external to the patient that contribute to injuries or health conditions, aiding in injury prevention and public health measures.
Laterality: Specification in ICD-10 indicating which side of the body is affected by a condition, important for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Benefits of ICD-10: Advantages of using ICD-10, such as improved accuracy in diagnoses, better data analysis, and enhanced communication among healthcare providers.
Limitations of ICD-10: Challenges associated with ICD-10, including complexity of coding, potential for errors, and variability in coding practices.
Exercises
Simulation Exercise: Mastering ICD-10 Coding
Objective: To practice selecting and applying appropriate ICD-10 codes for various clinical scenarios.
Materials Needed:
Access to ICD-10 codebook or online coding tool
Clinical scenarios (see examples below)
Paper or digital worksheet for recording code selections and reasoning
Instructions:
Introduction (5 minutes):
Briefly explain the purpose and importance of ICD-10 coding in healthcare.
Introduce the format of ICD-10 codes (e.g., three-character categories, specificity, etc.).
Demonstrate how to access and navigate the ICD-10 codebook or online tool.
Simulation (30 minutes):
Provide participants with a series of clinical scenarios (see examples below).
Participants should individually select the appropriate ICD-10 code(s) for each scenario based on the provided information.
Encourage participants to use the hierarchical structure of ICD-10 and the hierarchy principle to ensure accuracy and specificity.
Allow participants to ask questions or seek clarification as needed.
Discussion (15 minutes):
Review each scenario and discuss the selected ICD-10 codes.
Discuss the reasoning behind code selection, including considerations for specificity, laterality, and external causes if applicable.
Address any common challenges or misconceptions encountered during the exercise.
Summarize key points and emphasize the importance of accurate coding in healthcare settings.
Example Scenarios:
Scenario 1: A 45-year-old male presents with chest pain diagnosed as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Key Details: Patient’s age, gender, diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
ICD-10 Code(s): Select appropriate code(s) from the chapter on diseases of the circulatory system.
Scenario 2: A 30-year-old female presents with fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis is confirmed as pneumonia.
Key Details: Patient’s age, gender, symptoms, diagnosis of pneumonia.
ICD-10 Code(s): Select appropriate code(s) from the chapter on diseases of the respiratory system.
Scenario 3: A 60-year-old male undergoes knee replacement surgery due to severe osteoarthritis of the right knee.
Key Details: Patient’s age, gender, procedure (knee replacement surgery), diagnosis (osteoarthritis of the right knee).
ICD-10 Code(s): Select appropriate code(s) for both the diagnosis and the procedure from the relevant chapters.
Conclusion: This simulation exercise allows participants to apply their knowledge of ICD-10 coding in a practical and interactive manner. It reinforces the importance of accuracy, specificity, and thorough understanding of coding guidelines. Adjust the complexity of scenarios based on the participants’ familiarity with ICD-10 coding.
References
World Health Organization. (2022). International Classification of Disease (ICD). ICD Purpose and Uses. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classification-of-diseases
World Health Organization. (2016). International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10). Chapters, Categories, and Codes. Retrieved from https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/246208
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2023). International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM). Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coding-billing/icd-10-codes/2023-icd-10-cm
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2023). International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS). Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coding-billing/icd-10-codes/2023-icd-10-pcs
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2020). ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, Specificity in ICD-10. Retrieved from https://www.hhs.gov/guidance/document/icd-10-cm-official-guidelines-coding-and-reporting-fy-2019-0
World Health Organization. (2022). International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 11th Revision, Chapter XX: External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality: Accidents (V01-X59). Retrieved from https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en#/V01-X59
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). ICD-10-CM Official Coding Guidelines – FY 2021, Laterality Coding. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/icd/COVID-19-guidelines-final.pdf
Clinicspectrum. (n.d.). Introduction to ICD-9 and ICD-10 [Video]. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/x-BBn_bsUyU?si=OZ9vN_azUoC6dsJq
CMSHHSgov. (n.d.). Introduction to ICD-10 Coding [Video]. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/NNbTcMwrop8?si=Wd4dDRcjdxqT3lAY
Advancing the Business of Healthcare (AAPC). ICD-10 Conversion and Mapping. Retrieved from https://www.aapc.com/icd-10/conversion-mapping.aspx
CMSHHSgov. (n.d.). ICD-10 Coding and Diabetes [Video]. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/AEW2cXqXTSQ?si=Lk7iS4ssXgMXEXrn
